Django Forms§
Validate user input and return Python objects
Validate user input and return Python objects
Forms are composed of fields, which have a widget.
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
from django import forms
class ContactForm(forms.Form):
name = forms.CharField(label=_("Your Name"),
max_length=255,
widget=forms.TextInput,
)
email = forms.EmailField(label=_("Email address"))
Unbound forms don't have data associated with them, but they can be rendered:
form = ContactForm()
Bound forms have specific data associated, which can be validated:
form = ContactForm(data=request.POST, files=request.FILES)
Two ways to access fields on a Form instance
form.fields['name'] returns the Field objectform['name'] returns a BoundFieldBoundField wraps a field and value for HTML output
form.is_valid() triggers validation if neededform.cleaned_dataform.full_clean() performs the full cycle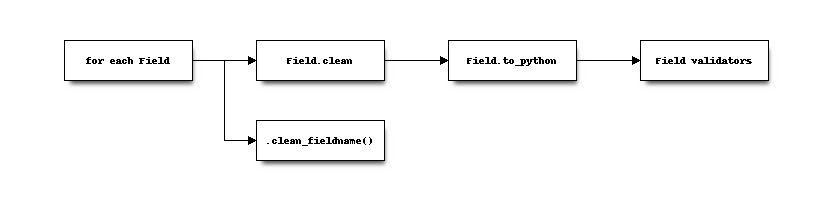
ValidationError.clean_fieldname() method is called after validatorsValidationErrorsThree primary "whole-form" output modes:
form.as_p(), form.as_ul(), form.as_table()<tr><th><label for="id_name">Name:</label></th>
<td><input id="id_name" type="text" name="name" maxlength="255" /></td></tr>
<tr><th><label for="id_email">Email:</label></th>
<td><input id="id_email" type="text" name="email" maxlength="Email address" /></td></tr>
<tr><th><label for="id_confirm_email">Confirm email:</label></th>
<td><input id="id_confirm_email" type="text" name="confirm_email" maxlength="Confirm" /></td></tr>
{% for field in form %}
{{ field.label_tag }}: {{ field }}
{{ field.errors }}
{% endfor %}
{{ form.non_field_errors }}
Additional rendering properties:
field.labelfield.label_tagfield.auto_idfield.help_text